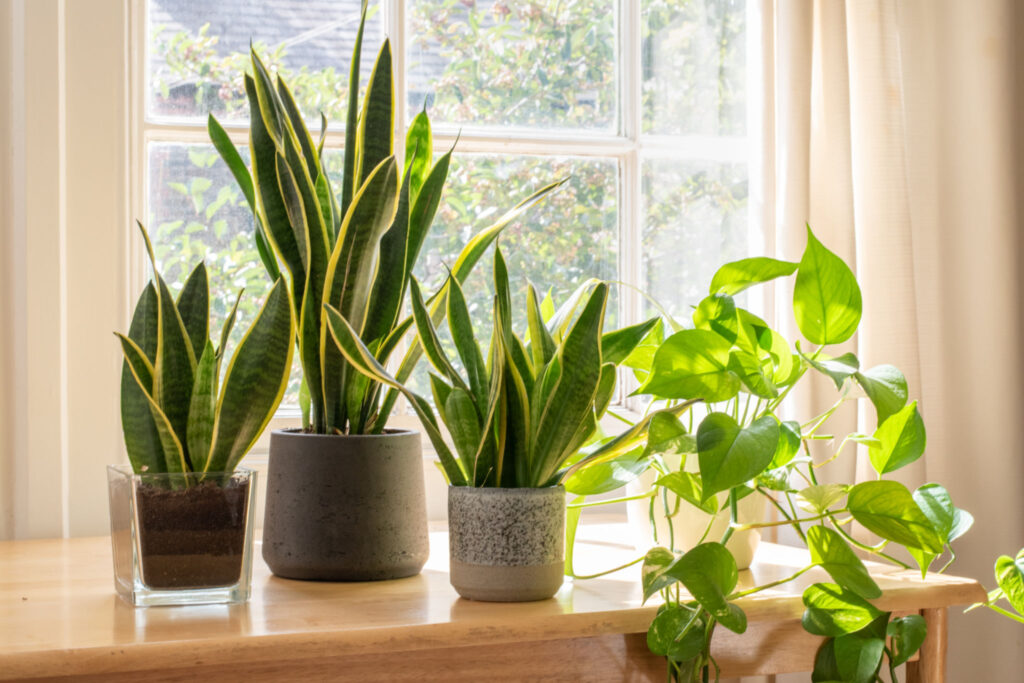
Indoor houseplants next to a window in a beautifully designed home or flat interior.
Overview of Snake Plants
Snake plants, also known as Sansevieria, are popular indoor houseplants characterized by their upright, sword-shaped leaves and low-maintenance nature. They belong to the succulent family and are native to tropical regions of Africa and Asia.
Benefits of Growing Snake Plants
Snake plants offer numerous benefits beyond their aesthetic appeal. They are renowned for their air-purifying properties, removing toxins such as formaldehyde, benzene, and xylene from indoor environments. Additionally, they require minimal care and can thrive in a variety of conditions, making them ideal for busy homeowners and beginners.
Factors Affecting Growth Rate
Several factors influence the growth rate of snake plants, including light exposure, temperature, humidity levels, soil quality, watering frequency, and pruning practices. By optimizing these conditions, you can encourage faster and healthier growth in your snake plants.
Creating Optimal Growing Conditions for Snake Plants
Light Requirements
Indirect Sunlight vs. Direct Sunlight
Snake plants prefer bright, indirect sunlight but can tolerate low light conditions. Avoid placing them in direct sunlight, as this can cause sunburn and damage the leaves. Instead, position them near a window where they can receive filtered sunlight throughout the day.
Duration of Light Exposure
Provide snake plants with 6-8 hours of light exposure per day for optimal growth. Rotate the plant occasionally to ensure even light distribution and prevent leaning or stretching towards the light source.
Temperature and Humidity
Ideal Temperature Range
Maintain temperatures between 60°F to 85°F (15°C to 29°C) for snake plants to thrive. They are tolerant of fluctuations but prefer warmer temperatures during the growing season and slightly cooler temperatures in the winter months.
Humidity Levels
Snake plants are adaptable to varying humidity levels but prefer moderate to high humidity. Increase humidity levels by placing a shallow tray filled with water and pebbles beneath the plant or using a room humidifier, especially during dry winter months.
Soil and Potting Medium
Well-Draining Soil
Use a well-draining potting mix specifically formulated for succulents or cacti to prevent waterlogged conditions and root rot. Add perlite or sand to improve drainage and aeration, promoting healthy root growth.
Pot Size and Type
Choose a pot with drainage holes to allow excess water to escape freely. Opt for a slightly larger pot than the plant’s current size to accommodate future growth without becoming overly root-bound.
Proper Watering and Fertilization Techniques
Watering Frequency and Method
Avoiding Overwatering
Snake plants are susceptible to root rot if overwatered, so it’s essential to allow the soil to dry out partially between waterings. Water the plant thoroughly, allowing excess water to drain away, and empty the saucer to prevent water accumulation.
Using Room-Temperature Water
Use room-temperature water to avoid shocking the plant’s roots. Allow tap water to sit for 24 hours to dissipate chlorine and other chemicals before watering, or use filtered water for best results.
Fertilization Schedule
Choosing the Right Fertilizer
Feed snake plants with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength during the growing season (spring and summer) every 4-6 weeks. Avoid fertilizing during the dormant period (fall and winter) to prevent nutrient buildup and potential damage to the plant.
Frequency of Feeding
Monitor the plant’s growth and adjust the fertilization schedule accordingly. Avoid over-fertilizing, as excessive nutrients can lead to salt buildup in the soil and damage the plant’s roots.
Pruning and Propagation Tips for Faster Growth
Removing Dead Leaves and Stems
Pruning Techniques
Regularly inspect the plant for dead or yellowing leaves and trim them close to the base using clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears. Removing dead foliage promotes airflow and encourages new growth.
Sterilizing Tools
Sterilize pruning tools before and after use to prevent the spread of diseases and pathogens. Wipe blades with rubbing alcohol or a disinfectant solution and allow them to dry thoroughly before pruning.
Propagation Methods
Leaf Cuttings
Propagate snake plants through leaf cuttings by carefully removing individual leaves and allowing them to callus over for a few days. Plant the cuttings in well-draining soil and keep them lightly moist until roots develop.
Division
Divide mature snake plants by carefully separating the rhizomes and roots into smaller sections. Plant each division in its own pot with fresh potting mix and water thoroughly. This method allows you to propagate multiple plants from a single parent plant.
Conclusion: Cultivating Healthy and Thriving Snake Plants
In conclusion, cultivating healthy and thriving snake plants requires careful attention to their specific growing requirements, including light, temperature, humidity, soil, watering, fertilization, pruning, and propagation. By creating optimal growing conditions and implementing proper care techniques, you can encourage faster growth and enjoy the beauty of lush, vibrant snake plants in your indoor space. Remember to observe your plants regularly and adjust your care routine as needed to ensure their continued health and vitality. With patience and dedication, you can cultivate a stunning collection of snake plants that will enhance your home or office environment for years to come.