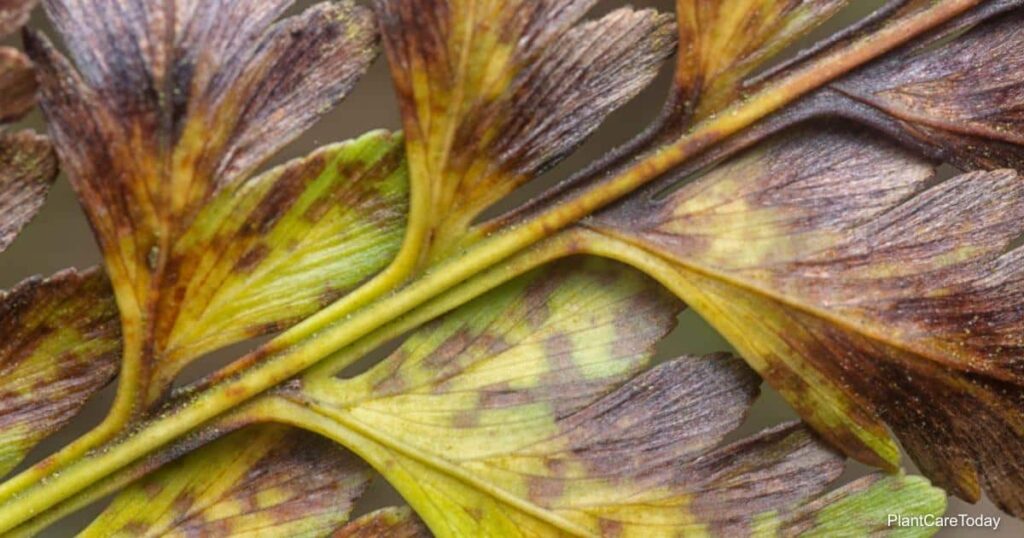
Maintaining lush green fern leaves adds a touch of elegance and vibrancy to any indoor or outdoor space. However, witnessing the gradual browning of fern leaves can be disheartening for plant enthusiasts. In this article, we’ll explore the common reasons behind why fern leaves turn brown and offer practical solutions to restore their health and vitality.
**Environmental Factors**
Environmental conditions play a significant role in the health of ferns, and inadequate humidity levels can contribute to the browning of leaves. Ferns thrive in environments with high humidity, mimicking their natural habitat in shaded forests. Exposure to direct sunlight can also lead to leaf scorching and browning, as ferns prefer indirect or filtered light. Additionally, extreme temperature fluctuations, especially during winter months, can stress ferns and cause leaf browning.
**Watering Issues**
Watering practices are crucial for maintaining healthy ferns, and both overwatering and underwatering can result in leaf browning. Overwatering can lead to root rot and oxygen deprivation, causing fern leaves to turn brown and wilt. Conversely, underwatering can result in dehydration and nutrient deficiency, manifesting as crispy, browned leaf tips. Furthermore, the quality of water used for irrigation can impact fern health, as chemicals such as chlorine and fluoride may be harmful to sensitive fern foliage.
**Soil Conditions**
Soil quality and composition directly affect the health of ferns, and poor drainage is a common culprit behind browned leaves. Ferns require well-draining soil to prevent waterlogging and root suffocation, which can result in leaf discoloration and deterioration. Nutrient deficiencies, particularly in essential minerals such as nitrogen, potassium, and magnesium, can also cause fern leaves to turn brown. Additionally, imbalanced soil pH levels can disrupt nutrient uptake and lead to leaf browning in ferns.
**Pest Infestations**
Pests can wreak havoc on ferns, causing damage to leaves and contributing to browning and deterioration. Common pests affecting ferns include spider mites, aphids, and scale insects, which feed on plant tissues and sap. Identifying pest infestations early is crucial for effective treatment, as severe infestations can lead to irreversible damage. Treatment options may include insecticidal soaps, neem oil, or biological controls, depending on the severity of the infestation. Implementing preventive measures such as regular inspections and proper plant hygiene can help deter pests and protect ferns from browning leaves.
In conclusion, understanding the underlying causes of browning fern leaves is essential for maintaining the health and vitality of these graceful plants. By addressing environmental factors, improving watering practices, optimizing soil conditions, and implementing pest management strategies, plant enthusiasts can restore their ferns to their former lushness and enjoy vibrant green foliage once again.